KASM Hacks
-
Users can access and use distant computer resources, such as operating systems and apps, from any device with internet connection thanks to a technology called virtual desktops. A specific virtual desktop environment called KASM (Kali Application Streaming Manager) was created for cybersecurity education. It offers a secure setting in which to learn and practice cybersecurity techniques, especially when using the Kali Linux operating system. Virtual desktops like KASM can be used in an AP CSP (Advanced Placement Computer Science Principles) environment to give students practical exposure with cybersecurity ideas and abilities without the need for costly hardware or running the risk of harming actual systems. In a safe and secure setting, students can learn and practice cybersecurity strategies to hone their skills.
-
My screenshots
AWS Database Hacks
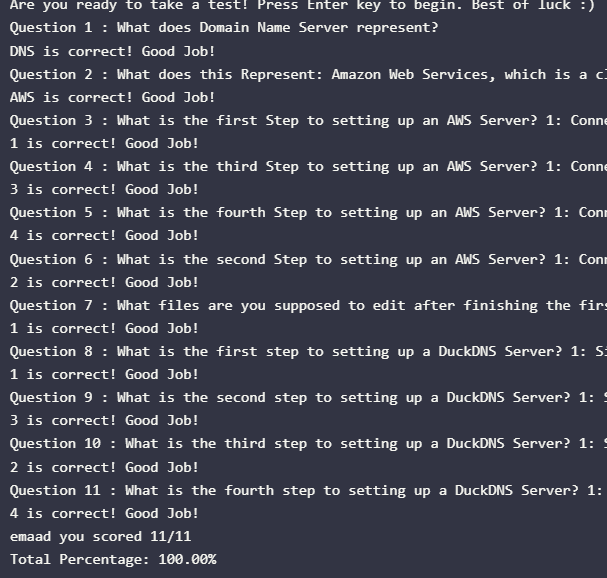
Quiz 1
- C
- A
- C
Quiz 2
- C
- D
- C
-
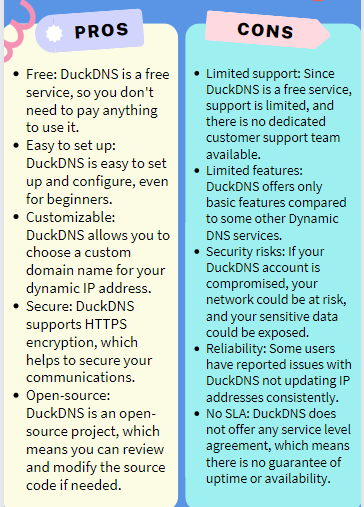
In order to access websites using domain names rather than IP addresses, DNS is required. DuckDNS is a free dynamic DNS solution that gives devices with changing IP addresses a reliable domain name. It is easy to set up and adaptable for a variety of purposes. Self-hosted services, remote access to home networks, and Internet of Things (IoT) projects can all use DuckDNS. Register for a free account, set up your router so that it updates your IP address with DuckDNS, and test your domain name to make sure it is functioning properly to set up DuckDNS. Overall, DuckDNS is a practical and cost-free choice for remote device access or hosting services at home.
-
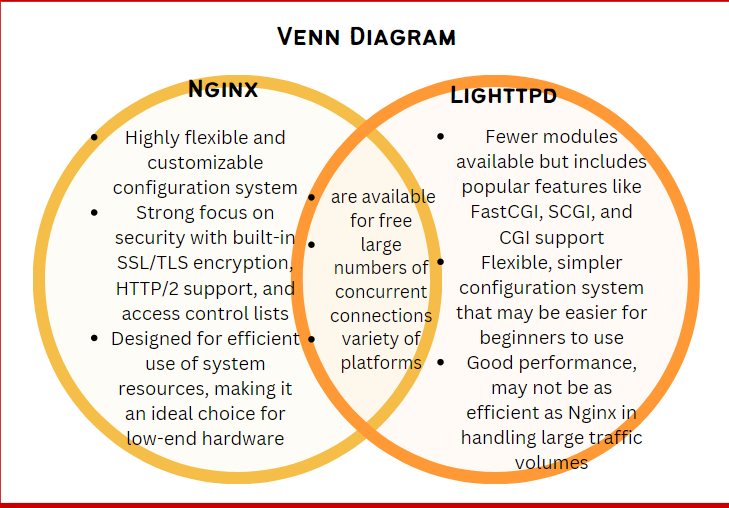
It’s critical to keep up with the most recent Nginx/Docker releases and to be aware of any deprecated functionality or modifications to the deployment procedure. Understanding the underlying technologies and industry standards for configuring and protecting your server is also beneficial.
Hack 6
Certbot Hacks
Two well-known open-source cryptography libraries used to implement SSL/TLS protocols in diverse applications estionsare OpenSSL and LibreSSL. Although they are similar, their security characteristics differ in some ways.
Since it has a wider codebase, OpenSSL has previously been subject to a number of high-profile security flaws, including Heartbleed (CVE-2014-0160) and DROWN (CVE-2016-0800), which were serious flaws that allowed for remote code execution and data leakage, respectively.
On the other side, LibreSSL is a fork of OpenSSL that was developed with the intention of offering a more up-to-date and secure implementation. It has a smaller codebase and places special emphasis on getting rid of obsolete and legacy code to minimize the attack surface. LibreSSL seeks to offer a safer alternative to OpenSSL as a result.
Both LibreSSL and OpenSSL have responsive security teams that quickly fix flaws through consistent updates and patches. In order to reduce risks, it is essential to keep both libraries updated to the most recent versions and adhere to best practices for safe implementation and configuration. This is because no program is fully impervious to vulnerabilities.